What are Panel Systems? Benefits, Types, and Uses Explained!
In recent years, the demand for innovative architectural solutions has led to the widespread adoption of panel systems across various industries. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global panel systems market is projected to reach $100 billion by 2025, driven by their versatile applications in commercial, residential, and industrial sectors. Panel systems not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of structures but also provide significant energy efficiency benefits, reducing operational costs by up to 30%.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority on modular construction, emphasizes the importance of panel systems in modern architecture, stating, "The integration of panel systems can transform conventional construction methods, yielding faster project completions and greater sustainability." This highlights a growing trend where builders are increasingly relying on panel systems for their ability to streamline construction processes while adhering to sustainability goals. As we explore the benefits, types, and uses of panel systems, it becomes evident that they are not just a passing trend, but a revolution in the way we approach building design and construction in today’s eco-conscious world.

Understanding Panel Systems: An Overview
Panel systems are versatile structural and architectural elements utilized across various industries. These systems consist of pre-fabricated panels made from materials such as wood, metal, or composite materials. They can be designed for load-bearing walls, facades, ceilings, and floors. The modular nature of panel systems allows for faster construction and ease of installation, making them an attractive option for builders and architects seeking efficiency in their projects.
The benefits of panel systems are numerous, including enhanced energy efficiency due to their ability to incorporate insulation and sustainable materials. Additionally, panel systems contribute to reduced waste and lower material costs, as they can be manufactured off-site and assembled on location. Various types exist, including curtain wall panels, structural insulated panels (SIPs), and pre-cast concrete panels, each serving specific building needs. Understanding the unique characteristics and applications of these panel types can aid in making informed decisions for construction and design projects, ensuring that they meet both functional and aesthetic requirements.
Benefits of Different Panel Systems
Key Benefits of Utilizing Panel Systems in Various Industries
Panel systems are increasingly popular across various industries due to their versatility and numerous advantages. One of the key benefits of utilizing panel systems is their ability to enhance efficiency in construction and manufacturing processes. By providing prefabricated solutions, these systems reduce on-site labor and construction time, allowing businesses to meet deadlines more effectively.
Additionally, panel systems contribute to sustainability efforts. Many types of panels are designed with eco-friendly materials, improving energy efficiency and reducing waste during production and installation. This is crucial for companies looking to minimize their environmental impact while maximizing productivity.
**Tips:** When considering panel systems for your project, evaluate the specific needs of your industry to choose the most appropriate type, such as structural, acoustic, or thermal panels. Always consult with experts to ensure proper installation and integration into existing frameworks, which can greatly affect performance and longevity.
Different Types of Panel Systems and Their Characteristics
Panel systems are versatile architectural elements widely used in construction and interior design. Among the various types of panel systems, we can categorize them into several key groups based on their characteristics: wall panels, ceiling panels, and flooring panels, each offering distinct functionalities and aesthetic appeals.
Wall panels, often made from materials like gypsum, timber, or composite materials, are designed to improve insulation and soundproofing. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the demand for wall panel systems is projected to reach USD 39.7 billion by 2026, driven by a growing emphasis on energy-efficient building solutions. Ceiling panels, which include acoustic and decorative options, offer both functional benefits — such as improving sound quality in spaces — and aesthetic enhancements. Lastly, flooring panels, such as laminate or engineered wood, are popular for their ease of installation and durability, with the global laminate flooring market expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.28% from 2021 to 2028.
These diverse panel systems cater to the specific needs of various applications, from residential homes to commercial buildings. Their characteristics, such as lightweight design, ease of maintenance, and sustainable materials, make them a preferred choice among architects and builders, contributing to the efficiency and innovation in modern construction practices.
Common Applications of Panel Systems in Modern Construction
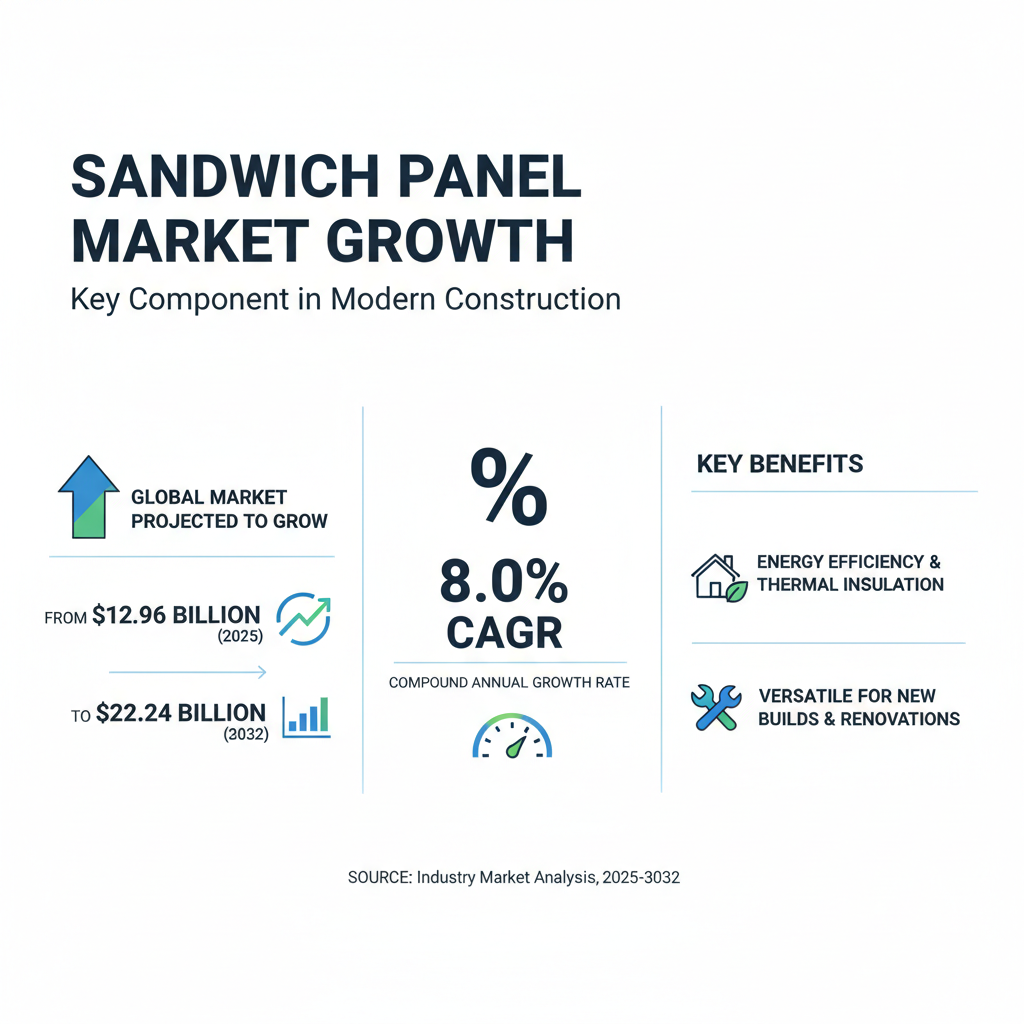
Panel systems are increasingly becoming a vital component in modern construction, offering various benefits aligned with industry trends. The global market for sandwich panels is projected to grow from $12.96 billion in 2025 to $22.24 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.0%. These systems are renowned for their energy efficiency, thermal insulation, and reduced construction time, making them a preferred choice for both new builds and renovations.
In addition to sandwich panels, the market for coated aluminum composite materials is also on a steep upward trajectory, forecasted to rise from $31.97 billion in 2025 to $68.86 billion by 2034, with an impressive CAGR of 8.9%. These materials are often used for facades, offering aesthetic flexibility and durability. Furthermore, the architectural acoustic panel market is set to expand significantly, with expectations of increasing from $8.26 billion in 2024 to $12.26 billion by 2032, translating to a 5.0% CAGR. This growth indicates a rising awareness of sound management in interior spaces, further accentuating the versatility and application of panel systems in contemporary construction practices.
Comparative Analysis of Panel Systems vs. Traditional Building Methods
Panel systems have gained traction in modern construction, often heralded for their efficiency and versatility compared to traditional building methods. While traditional methods like brick and mortar rely heavily on labor and time, panel systems streamline the building process through modular designs. This allows for quicker assembly and reduced on-site labor, which can significantly cut down construction costs.
When considering panel systems versus traditional building methods, one should weigh the specific requirements of the project. For instance, panel systems may be better suited for structures needing rapid construction, like temporary facilities or emergency housing. However, for more complex architectural designs where individual craftsmanship is paramount, traditional methods may still hold an advantage.
**Tips:** If you choose to use panel systems, ensure you have a reliable supplier who can provide quality materials that meet your design specifications. Furthermore, always account for local building codes and regulations, as they can influence the feasibility of using panel systems in your project. Finally, consider engaging with a contractor experienced in panel systems to maximize their benefits during installation.
What are Panel Systems? Benefits, Types, and Uses Explained!
| Dimension | Panel Systems | Traditional Building Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Construction Speed | Fast installation, several panels can be assembled in days | Slower; often takes weeks to months |
| Energy Efficiency | High insulation properties reduce energy costs | Variable efficiency depending on materials used |
| Weight | Lightweight panels reduce structural load | Heavier materials may require more robust foundations |
| Design Flexibility | Can be customized in numerous designs and finishes | Limited design options due to material constraints |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Potentially lower labor and material costs | Higher costs due to longer construction times |
| Environmental Impact | Often uses sustainable materials and methods | Varies widely, potential for high waste |
| Maintenance | Generally low maintenance and durable | May require ongoing upkeep depending on materials |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 10 Innovative Steel Metal Products Redefining Industry Standards
-

How to Choose the Best Composite Deck Joists for Long-lasting Durability and Performance
-

What is Steel Framing and How It Transforms Construction Efficiency and Durability
-

2025 How to Choose the Right Exterior Sheathing for Your Home
-

How to Choose Cold Formed Metal Framing for Your Construction Project
-

2025 Top 10 Panel Installation Trends You Need to Know for Your Home
